
The English language belongs to the Indo-European language family, which includes languages spoken by over three billion people. This means that English is related to languages like German and Dutch.
There are many different dialects of English, and the language has evolved over time. English is a West Germanic language, and it was first spoken in England. The language has also been greatly influenced by other languages throughout its history, including Latin, French, and Norse.
English is now the most widely spoken language in the world, and it is the official language of many countries. It is also one of the most popular choices for second-language learners. If you're interested in learning more about the English language family, keep reading. Below, we dive into the subject, answering the most intriguing questions.
Learn English with Langster
What Is a Language Family?
A language family is a group of languages that share a common ancestor. The Indo-European language family, for example, includes languages like English, German, and Dutch. All of these languages are closely related and share the same language family because they descended from a common ancestor.
Languages can be related in different ways. For instance, two languages might share the same root words or grammar structures. Languages can also be related because they have borrowed words from each other. For example, English has borrowed many words from French.
Languages can change over time, and new languages can emerge from existing ones. For instance, English is a descendant of the West Germanic language family. The English language has also been influenced by other languages throughout its history.
For instance, the Norman Conquest of England in 1066 led to the introduction of French words into the English language. Later, during the Middle Ages, Norse invaders brought their language to England, which also had an impact on English.
If you want to learn more about Old and Middle English, as well as how Modern English was formed, we explore these influences in greater detail in our post dedicated to the history of the English language. Check it out!
What Is the Largest Language Family in the World?
The Indo-European language family is the largest of the 142 different language families in the world. It includes over 400 languages and dialects spoken by over three billion people, with 46% of the world’s population having a native language in this family. Indo-European languages are dominant in Europe as well as Central, Western, and South Asia.
The Indo-European language family is further divided into several branches, including but not limited to:
- Romance languages, which include French, Italian, Spanish, and Portuguese, with more than 900 million native speakers worldwide. These languages are all descended from Latin, which was the language of the Roman Empire.
- Slavic languages, including Russian, Polish, and Czech, spoken by over 400 million people.
- Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, and Afrikaans, spoken by approximately 515 million people.
- Celtic languages include Irish, Welsh, and Scottish Gaelic, with about two million of both native and non-native speakers.
- Iranian languages, including Persian and Pashto, with over 45 million speakers.
- Indo-Aryan languages include Hindi, Bengali, and Punjabi. The Indo-Aryan languages are spoken by over one and a half billion people.
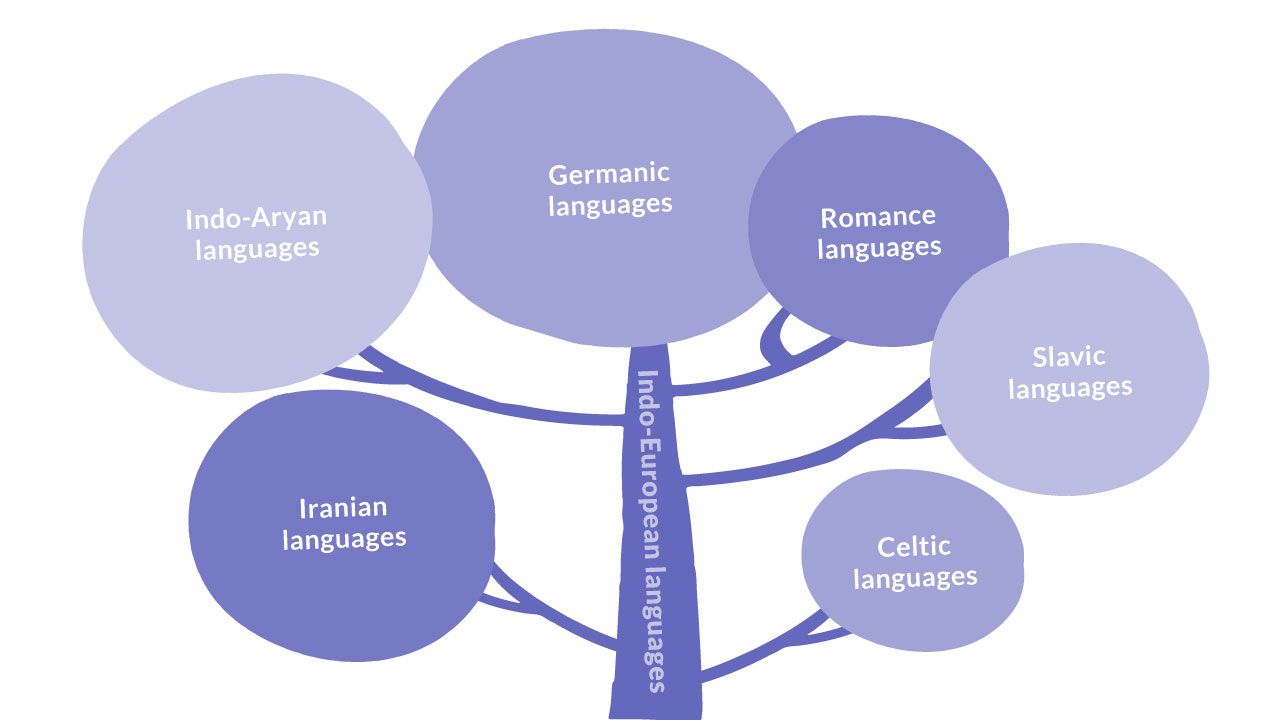
The English language belongs to the West Germanic branch of the Indo-European language family. Other Germanic languages are German, Dutch, and Afrikaans, but the family also includes the Nordic and Scandinavian languages. These languages are spoken in northwestern Europe, and they share some common features.
For example, West Germanic languages use the Latin alphabet and have similar sound systems. They also have similar grammar structures. However, there are some important differences between these languages.
For instance, German has three genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), while English nouns aren't gendered at all. German also has a different word order than English. The verb in German can be in the second position (most common), initial position (verb first), or clause-final position, while in English, the verb always comes after the subject.
Geographic Distribution
Indo-European languages are spoken all around the world. The Romance languages, for example, are spoken in Europe, South America, and Africa. Slavic languages are spoken in Eastern and Central Europe, while Germanic languages are spoken in North America, Europe, and Oceania.
Celtic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, and Wales. Iranian languages are spoken in Iran and Afghanistan, and Indo-Aryan languages are spoken in India and Pakistan.
The English language, as part of one of the largest language families, is spoken in many different countries around the world. It is the official language of countries like the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and other Commonwealth countries.
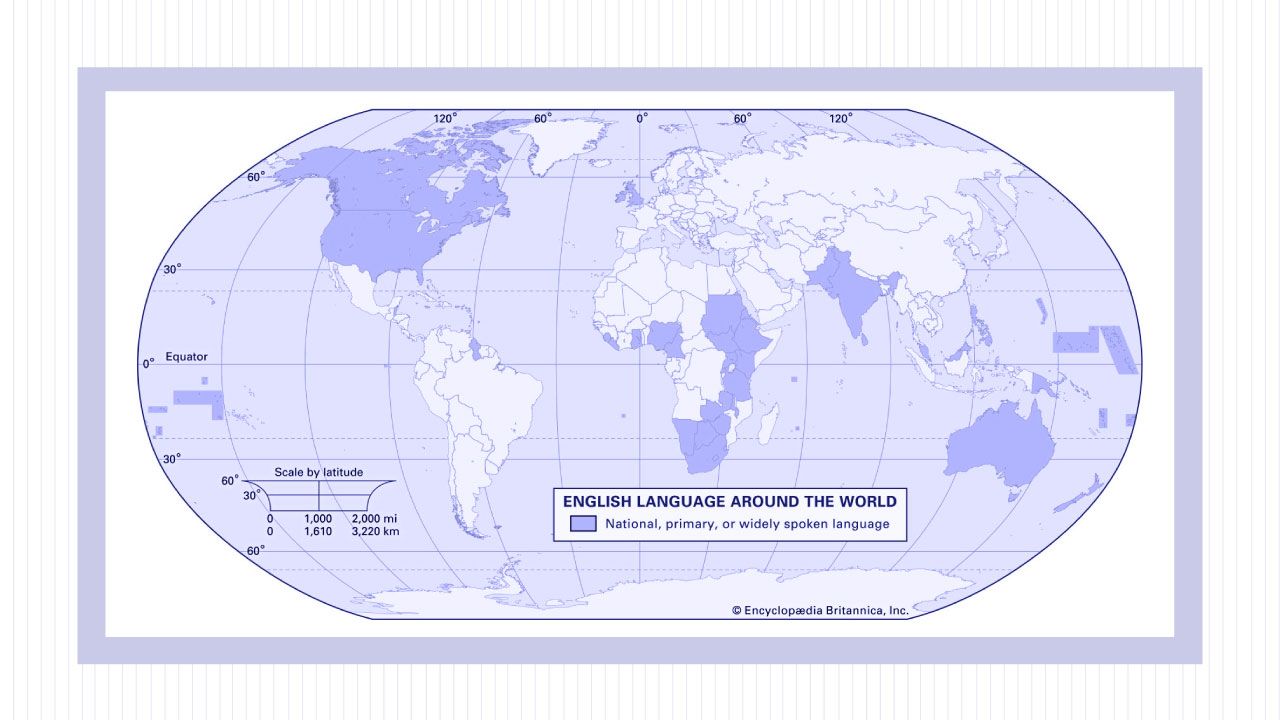
English is also one of the official languages of the European Union and many other international organizations.
There are several reasons why the English language has become so widespread. One reason is the British Empire. At its height, the British Empire was the largest empire in history, and it spread the English language to all corners of the globe.
Another reason for the global spread of English is American pop culture. American movies, TV shows, and music are popular all over the world, while using English as their dominant language.
Furthermore, English is the language of the internet. Over half of all web content is in English, so it’s no surprise that many people learn English so they can access this huge wealth of information, both for professional and recreational purposes.
The English Language Family Tree: Varieties and Dialects
The English language has a lot of varieties that can be divided into two groups – inner circle varieties and outer circle varieties.
Inner circle varieties are spoken in countries where English is the native language, like the UK, the US, and Commonwealth countries. Outer circle varieties are spoken in countries where English is not the native language but is used for official purposes like education or government.
For instance, the most common varieties of English are British English, American English, Canadian English, and Australian English. There are also several African varieties of English, like Nigerian English and South African English.
On the other hand, English is also spoken as a second language in many non-English speaking countries around the world. In some countries, like India and Singapore, English is used as a lingua franca – a common language that is used for communication between speakers of different languages.
To make things a little more confusing, there are also standard and non-standard dialects of English, which can differ from region to region. Dialects can differ in pronunciation and vocabulary, but rarely in grammar.
The standard dialect of English is known as Received Pronunciation or RP. RP is considered the “correct” way to speak English, and it is often used by news announcers and other public figures, for which it frequently is referred to as the Queen's English, Oxford English, or BBC English.
RP denotes what is traditionally considered the standard accent of people living in London and the southeast of England. RP is not necessarily the most common form of English, but it is the dialect that is considered standard for British English.
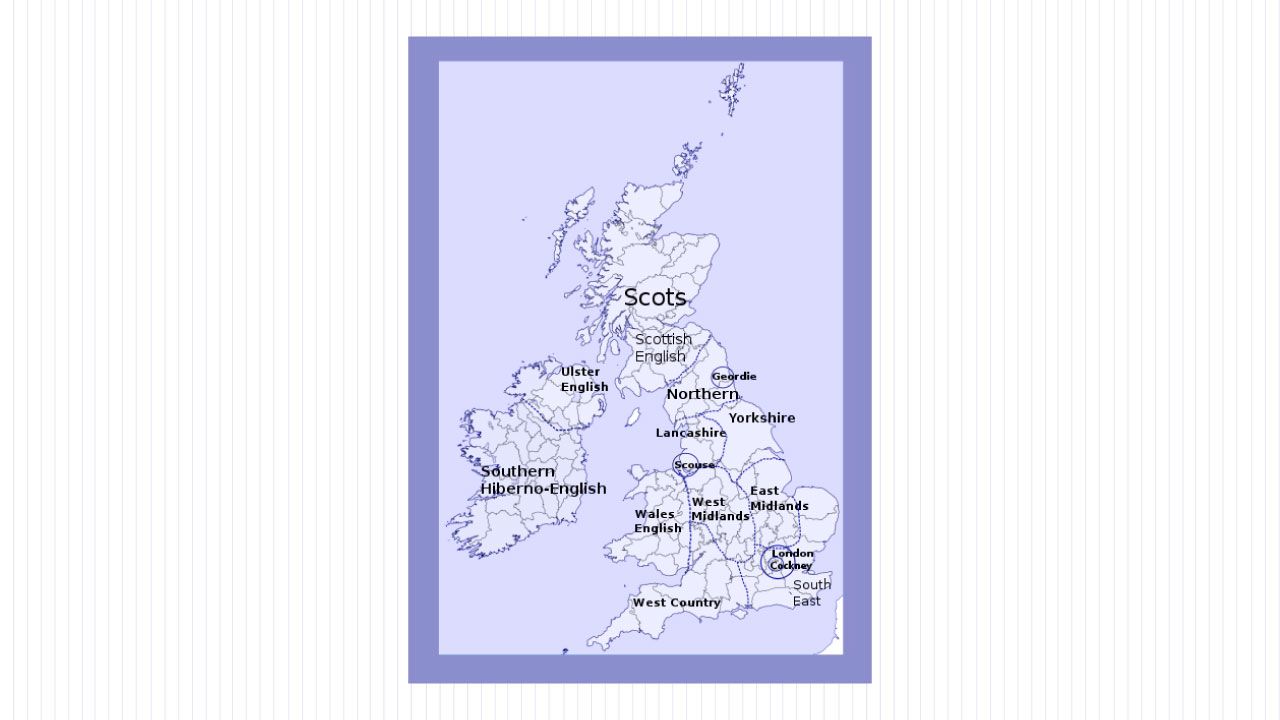
The term “non-standard English,” on the other hand, refers to any dialect of English that is not RP. Non-standard varieties of English are often spoken in specific regions, such as the United States, Ireland, or Australia. These dialects can vary widely, and they often have their own unique words, phrases, and slang.
For instance, people from the United States might say “trash can” while people from England would say “dustbin.” Australians might use the word “esky” to refer to a cooler, while people from other parts of the world would say “cooler box.” Here, you can check more differences between British and American English.
Furthermore, British English itself has many different dialects, like Scottish English, Irish English, and Cockney English. American English also has a lot of different dialects, like Southern American English, Boston English, and African American Vernacular English.
Despite the many differences between standard and non-standard English, all dialects of English are mutually intelligible. This means that people from any English-speaking country can understand each other, even if they have different ways of speaking.
So, whether you speak RP or a non-standard dialect of English, you can be sure that people from all over the world will be able to understand you!
The Bottom Line

As you can see, the English language is quite complex. It has a long history filled with many factors that influenced its development. The English language is also spoken in many different countries, which has led to the development of various dialects.
While English may be a complex language, it is also one of the most widely spoken languages in the world. So, whether you're a native speaker or you're just learning English, there are plenty of people out there who can help you practice!
You can also download our Langster app and practice proper phasing with audio from native English speakers. Good luck!









